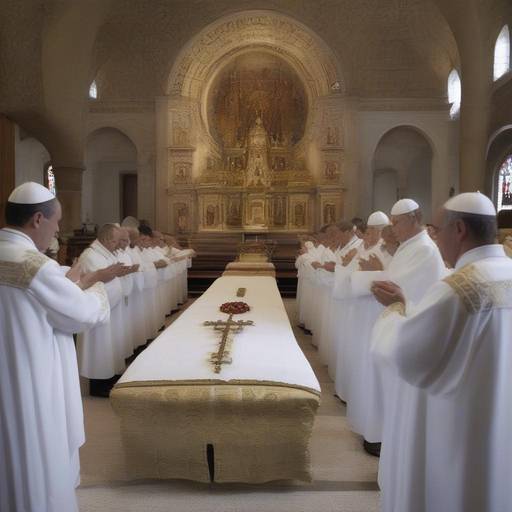
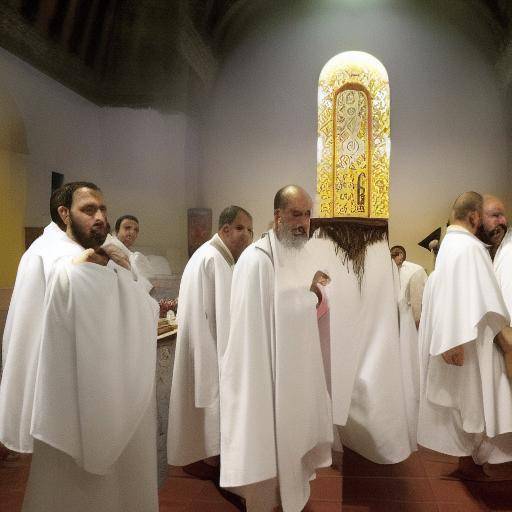
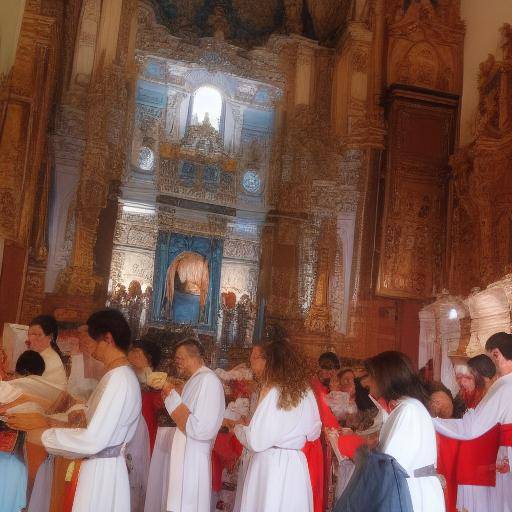
The Depth and Meaning of the Sacred Rites
In Hindu culture, initiation rites are a fundamental part of marking the beginning of different stages in a person's life. These rituals are full of meaning and symbolism, and play a crucial role in the lives of Hindus. In this article, we will explore in depth the rites of initiation into Hindu culture, its importance, evolution over time, as well as its similarities and differences with other rituals. We will also highlight the connection between initiation rites and Hindu culture, providing a complete view of this ancestral practice that remains relevant today.
Introduction
The Relevance of the Rites of Initiation in Hindu Culture
The rites of initiation, known as "samskaras", are ceremonies that mark the beginning of each important stage of a person's life in Hindu culture. From birth to death, these rituals play a crucial role in the spiritual and social development of an individual. As we deepen the understanding of these rituals, we discover that they possess significant wealth that goes beyond merely symbolic.
In this article, we will immerse ourselves in the history and meaning of the rites of initiation into Hindu culture, exploring its evolution over time and its profound connection with the beliefs and traditions of this ancient civilization. In addition, we will analyze rituals in the context of Hindu culture, comparing them with other traditions and providing a broad perspective on their importance and relevance today.
History and Background
Ancestral Origins and Development of Initiation Rites
The rites of initiation have ancestral roots and are deeply rooted in Hindu culture. Since time immemorial, these rituals have been regarded as fundamental pillars in the life of an individual, marking their integration into different stages of life. The ancient texts such as the Vedas and the Brahmanas contain detailed references to the samskaras, showing their importance in Hindu society since ancient times.
The rites of initiation evolved over the centuries, adapting to social and cultural changes, but maintaining its fundamental essence. Throughout history, different dynasties and rulers have contributed to the evolution of these rituals, adding layers of meaning and complexity. Even in the modern era, the rites of initiation remain an integral part of the daily lives of Hindus, serving as cultural anchors that keep the heritage of generation to generation alive.
Analysis in Deep
Meaning and Value of Initiation Rites
The rites of initiation into Hindu culture embody a symbolic and spiritual richness that transcends the merely ceremonial. These rituals not only mark the beginning of a stage of life, but also establish a profound connection with tradition, spirituality and community. Moreover, such rituals provide a solid basis for the moral and ethical development of an individual, instilling fundamental values at every crucial stage of life.
In exploring the rites of initiation into Hindu culture, it is vital to understand its relevance in contemporary society. Although traditions have evolved, the essence and importance of initiation rituals have endured over time, consolidating their position as fundamental pillars in the lives of Hindus. The intrinsic nature of these rituals represents a continuous connection with cultural and spiritual heritage, offering a unique perspective that transcends mere formalism.
Comprehensive review
Contemporary Importance of Initiation Rites
Despite modern challenges and sociocultural changes, the rites of initiation into Hindu culture remain relevant in people's lives. These rituals not only strengthen family and community ties, but also infuse a sense of identity and belonging. In addition, they provide a sacred and transcendental dimension to the transitions of life, giving meaning and purpose to each crucial stage.
In addition, the initiation rites in Hindu culture provide a solid framework for the transmission of intergenerational knowledge and values. As traditions intertwine with modern life, these rituals not only preserve ancestral wisdom, but also serve as beacons that guide future generations on their journey to personal and spiritual realization.
Comparative analysis
Similarities and Differences with Other Rituals
By comparing the rites of initiation into Hindu culture with other passing rituals in different cultures, a wealth of perspectives and practices emerge that reveal the complexities of human condition. While there is a diversity of ritual expressions around the world, the parallels in the intent and function of these rites are evident. Transition, transformation and evolution are universal themes that find echo in a variety of ceremonies and rituals in different cultures.
The main distinction that characterizes the rites of initiation into Hindu culture is its deep roots in Hindu spirituality and worldview. While many passing rituals in other cultures focus on the transition to specific social roles, Hindu initiation rites transcend the social, embracing a holistic understanding of human existence, which incorporates both the earthly dimension and the transcendent.
Practical Tips and Recommendations
Nutrite the Meaning and Value of Initiation Rites
For those who wish to integrate the rites of initiation into Hindu culture into their spiritual and family practice, it is essential to understand and appreciate the depth and meaning of these rituals. The observance of the samskaras not only involves following the ritual steps, but also cultivating a holistic understanding of their meaning and value in the life of oneself and the community.
By participating in the rites of initiation, it is crucial to commit to a process of consciousness and reflection that honors the connection between the material and the spiritual, the individual and the collective, and the temporal and the timeless. In doing so, a space for transformation and growth is opened in the context of a rooted tradition that has resisted the test of time and remains relevant today.
Industry Perspectives and Expert Reviews
Future Vision of Initiation Rites in Hindu Culture
Experts and academics agree that the rites of initiation into Hindu culture will maintain their relevance and meaning in the future, serving as cultural anchors in a constantly changing world. In addition, it is expected that these rituals will continue to evolve to address contemporary challenges, keeping ancestral traditions alive while adapting to the realities of the twenty-first century.
The need to preserve and revitalize the rites of initiation into Hindu culture becomes even more pressing in an era characterized by globalization and rapid technological evolution. In this sense, initiation rites offer a moral and spiritual compass that can offer a meaningful guide and anchor in an increasingly interconnected and changing world.
Conclusion
Celebrating the Depth of Initiation Rites in Hindu Culture
The rites of initiation into Hindu culture exemplify the richness, depth and meaning that emanates from ancestral traditions. As we explore history, symbolism, contemporary importance and connection with spirituality and community, it is clear that these rituals transcend time and space, encapsulating timeless wisdom that remains relevant in modern life.
The intrinsic value of the rites of initiation into Hindu culture lies in its ability to unite the eternal with the ephemeral, the material with the spiritual, infusing every stage of life with meaning, purpose and transcendence. Through its continuous and reflective observance, we can find a deep appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life, thus honoring the continuity of tradition and the transcendence of human existence.
FAQs
1. What are some of the most outstanding initiation rites in Hindu culture?
Prominent initiation rites in Hindu culture include Nama-karana (child's name), Annaprashana (gender food), Upanayana (sacred thread ceremonies), Vivaha (matrimony) and Antyeshti (fair ritual).
2. How do the rites of initiation influence the daily life of a Hindu individual?
The rites of initiation significantly influence the daily life of a Hindu, as they mark important milestones in their spiritual, social and religious development. These rituals provide a guide to live a meaningful life in harmony with ancestral teachings.
3. What is the role of spirituality in Hindu initiation rites?
Spirituality is a central component in Hindu initiation rites, since these rituals not only celebrate the physical transitions of life, but also mark the spiritual and moral growth of a person. They also foster a deep connection with the sacred and transcendent.
4. How have initiation rites evolved over time?
Throughout history, initiation rites have evolved to adapt to sociocultural changes, keeping their fundamental essence. As society and technology have advanced, initiation rituals have integrated contemporary elements without compromising their spiritual and cultural relevance.
5. What is the importance of preserving the rites of initiation into Hindu culture?
The preservation of the rites of initiation is crucial to keeping alive the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of India. These rituals not only maintain the connection with ancestral traditions, but also provide a sense of identity and belonging to the Hindu community.
6. What is the impact of initiation rites on family and community life?
The rites of initiation strengthen family and community ties by celebrating and sharing important milestones in a person's life. These rituals foster social cohesion, transmit values and unite the community in a sense of continuity and shared purpose.
In conclusion, the rites of initiation into Hindu culture offer a window to the spiritual, cultural and social wealth of one of the oldest civilizations in the world. These rituals, rooted in tradition and spirituality, continue to play a central role in the lives of Hindus, providing meaning, transcendence and continuity through the various stages of human existence. Their reflective observance and deep understanding not only enriches individual life, but also preserves the very essence of a millennial heritage for future generations.